KOI冰球人机大战
项目简介
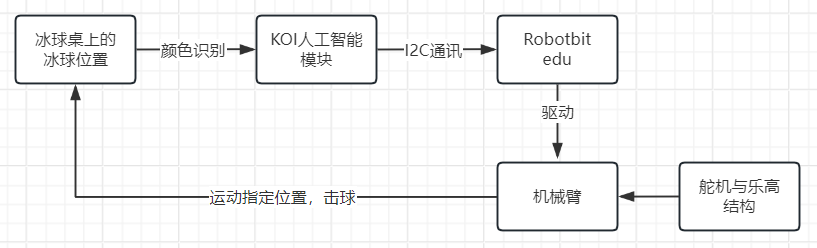
该项目旨在利用小喵科技出品的AI摄像头KOI模块构建一个冰球机器人,实现人机对战的游戏。
玩家可以与机器人对战,通过KOI的摄像头,通过颜色识别,捕捉冰球的位置,然后利用两个大舵机控制机械臂来击打冰球,使其进入对方的球门,从而得分。
此项目中KOI作为主控,识别出冰球位置,再通过I2C通讯,控制Robotbit上的的舵机驱动电路,进而实现反馈与控制。
这个项目结合了计算机视觉、机器人控制和游戏设计等方面的技术,是一个有趣而具有挑战性的创意项目。
项目清单
- K210 AI摄像头模块
- Robotbit edu扩展板
- Geekservo 5KG舵机
- 冰球桌整套(含冰球)
- 部分乐高结构和3D打印件
- 连接线
- 电源
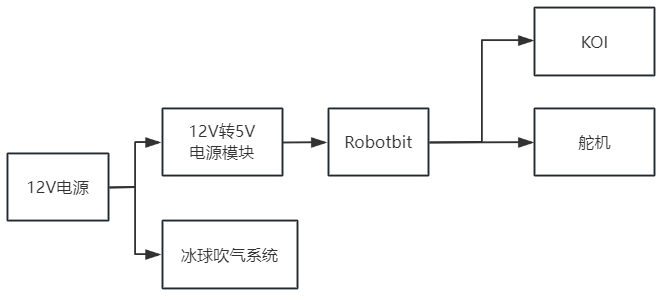
项目框图
实现步骤
步骤概况
- STEP1:结构搭建
- STEP2:硬件连接
- STEP3:电源接线
- STEP4:程序下载
- STEP6:程序运行
STEP1:结构搭建
安装舵机结构
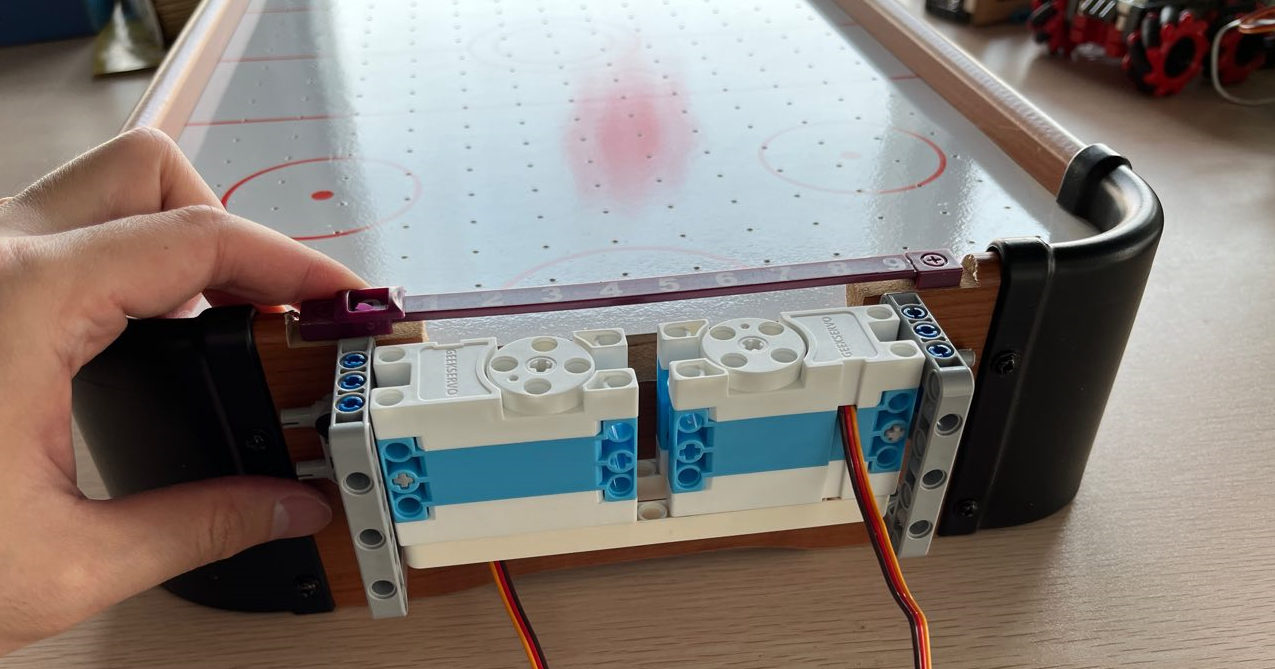
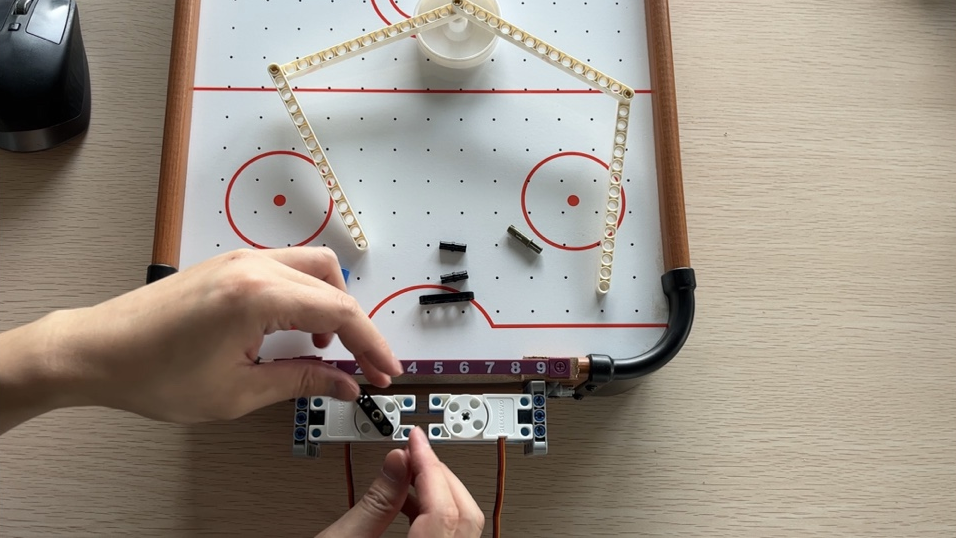
安装摇臂和击球打印件
<<<<<<< HEAD

=======
63cbd0fa740666551a964a4be4cf69748237c39c 安装立柱(用于固定KOI摄像头和Robotbit扩展板)
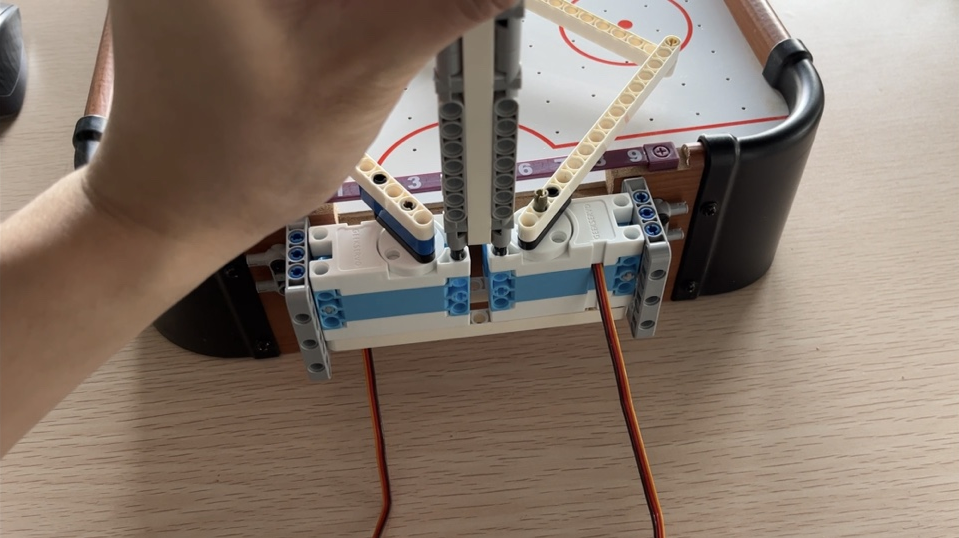
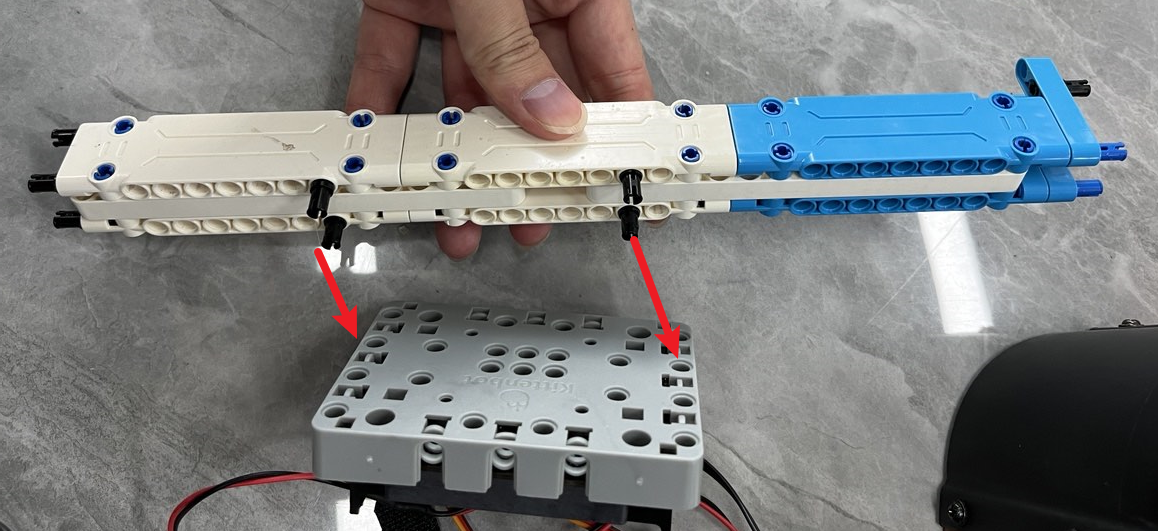
把电控部分安装到结构上
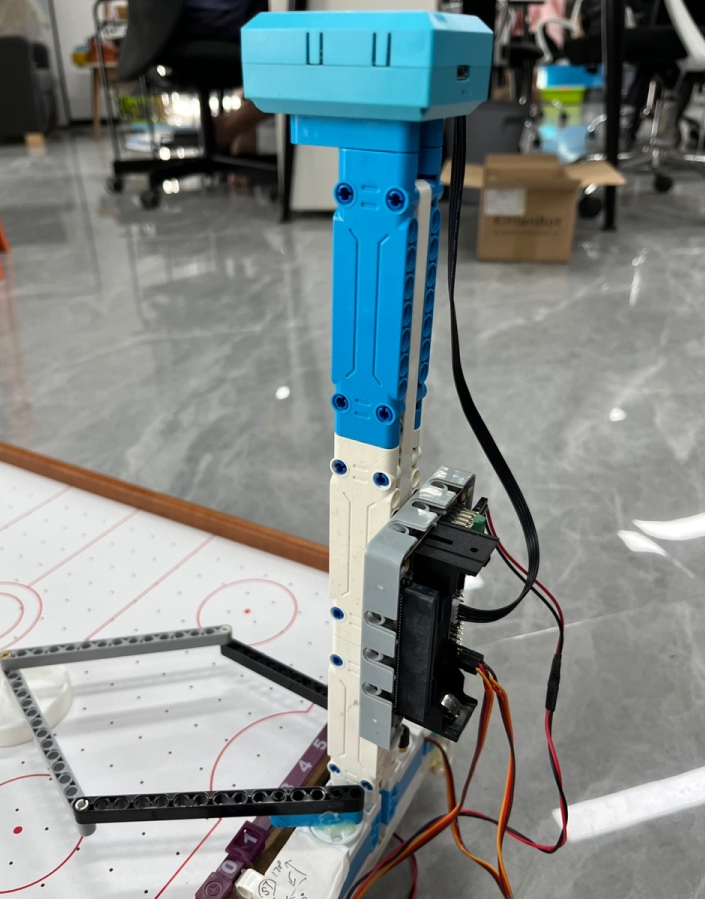
搭建完成
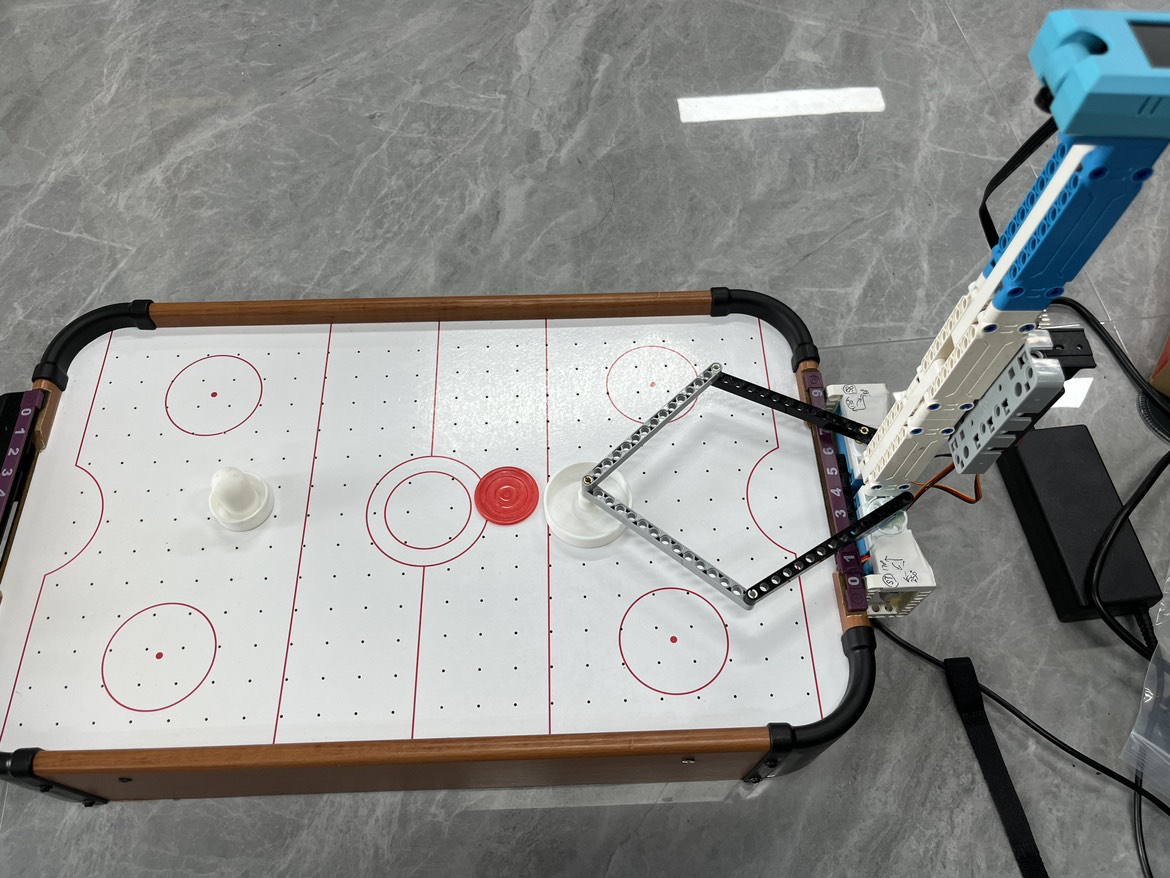
STEP2:硬件连接
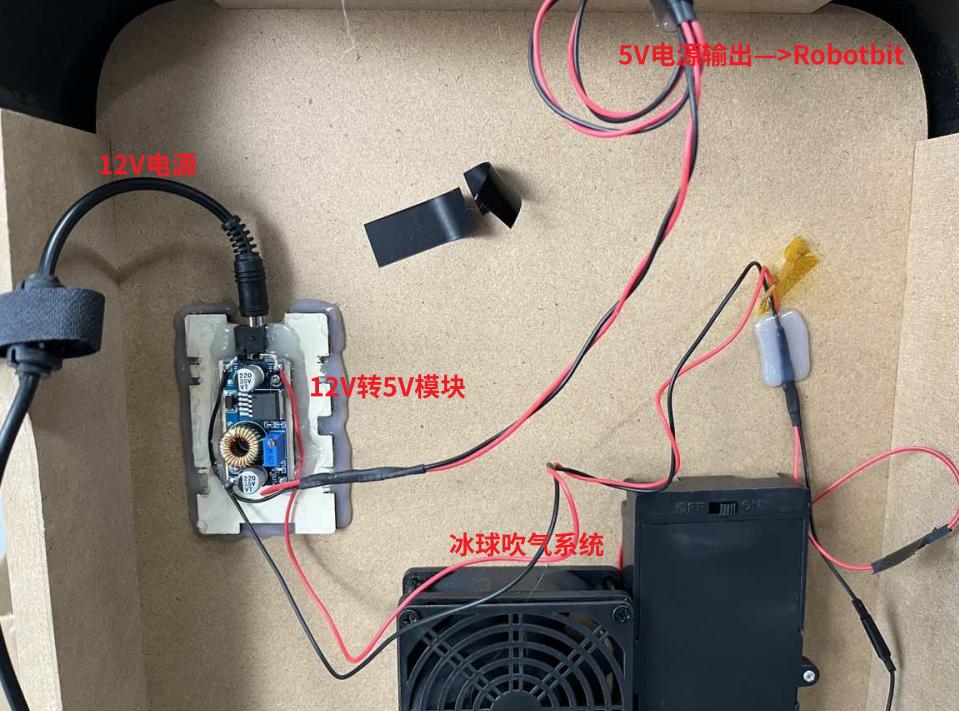
根据图示说明进行接线
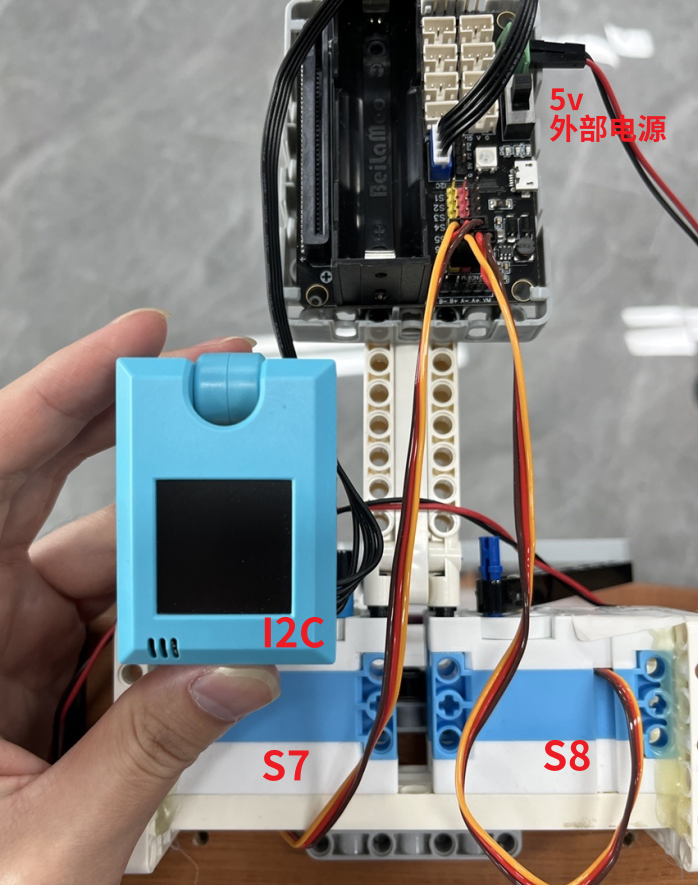
STEP3:电源接线
采用外部12V电源给整个系统进行供电
实物接线示意:
STEP4:程序下载
拿一张金士顿的TF卡(推荐京东官方品牌店购买),容量8G或者16G都可以
把我们提供的main.py程序文件,复制到TF卡中在再把TF卡插到KOI模块上。

main.py内容如下:
#适用于koi2 硬件版本v3(大摄像头版本)
import sensor, image, time, lcd, utime
import math, ustruct
from maix import KPU, GPIO, I2S
from machine import UART, I2C
from fpioa_manager import fm
import gc
grid = [
(56,74),(96,74),(137,72),(179,70),(220,68),(262,67),
(52,113),(94,116),(136,112),(179,109),(222,107),(264,104),
(51,157),(93,156),(139,154),(181,151),(227,150),(269,147),
]
PCA9685_ADDRESS = 0x40
MODE1 = 0x00
MODE2 = 0x01
SUBADR1 = 0x02
SUBADR2 = 0x03
SUBADR3 = 0x04
PRESCALE = 0xFE
LED0_ON_L = 0x06
LED0_ON_H = 0x07
LED0_OFF_L = 0x08
LED0_OFF_H = 0x09
ALL_LED_ON_L = 0xFA
ALL_LED_ON_H = 0xFB
ALL_LED_OFF_L = 0xFC
ALL_LED_OFF_H = 0xFD
S1 = 0x1
S2 = 0x2
S3 = 0x3
S4 = 0x4
S5 = 0x5
S6 = 0x6
S7 = 0x7
S8 = 0x8
RESTART = 0x80
SLEEP = 0x10
ALLCALL = 0x01
INVRT = 0x10
OUTDRV = 0x04
RESET = 0x00
positions = [
[240, 195], [235, 175], [220, 155], [210, 135], [190, 125], [160, 115],
[260, 190], [250, 165], [235, 145], [220, 125], [195, 105], [170, 95],
[285, 190], [275, 170], [250, 140], [220, 105], [195, 85], [170, 70]
]
class RobotBit:
def __init__(self):
self.address = PCA9685_ADDRESS
self.i2c = I2C(I2C.I2C0, freq=400000, scl=17, sda=14, addr_size=7)
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, RESET])) # reset not sure if needed but other libraries do it
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, RESET]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE2, OUTDRV]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, ALLCALL]))
time.sleep_ms(5)
mode1 = self.i2c.readfrom_mem(self.address, MODE1, 1)[0]
mode1 = mode1 & ~SLEEP # wake up (reset sleep)
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, mode1]))
time.sleep_ms(5)
self.set_pwm_freq(50)
self.inited = True
def set_pwm_freq(self, freq_hz):
"""Set the PWM frequency to the provided value in hertz."""
prescaleval = 25000000.0 # 25MHz
prescaleval /= 4096.0 # 12-bit
prescaleval /= float(freq_hz)
prescaleval -= 1.0
prescale = int(math.floor(prescaleval + 0.5))
oldmode = self.i2c.readfrom_mem(self.address, MODE1, 1)[0]
newmode = (oldmode & 0x7F) | 0x10 # sleep
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, newmode]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([PRESCALE, prescale]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, oldmode]))
time.sleep_ms(5)
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([MODE1, oldmode | 0x80]))
def set_pwm(self, channel, on, off):
"""Sets a single PWM channel."""
if not self.inited:
self.initRobotBit()
if on is None or off is None:
data = self.i2c.mem_read(4, self.address, LED0_ON_L+4*channel)
return ustruct.unpack('<HH', data)
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([LED0_ON_L+4*channel, on & 0xFF]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([LED0_ON_H+4*channel, on >> 8]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([LED0_OFF_L+4*channel, off & 0xFF]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray([LED0_OFF_H+4*channel, off >> 8]))
def geekServo(self, index, degree):
# 50hz: 25,000 us
# 500~2650us->0~360
# v_us = degree * 50 / 9 +500
v_us = 200/36*degree + 500 # calibrated
value = int(v_us*4096/20000)
self.set_pwm(index+7, 0, value)
class AirHockey:
def __init__(self):
self.thresholdMap = {
'red': [30,100,15,127,15,127],
'blue': [0,50,-64,64,-127,-20]
}
sensor.reset()
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA)
lcd.init()
lcd.rotation(0)
lcd.clear()
sensor.set_vflip(True)
sensor.set_hmirror(True)
sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000)
self.displayGrid()
self.cachedPosition = []
self.t0 = time.ticks_ms()
self.lastIndex = -1
self.robo = RobotBit()
def displayGrid(self):
self.img = sensor.snapshot()
for i in range(len(grid)):
self.img.draw_cross(grid[i][0],grid[i][1],5,color=(0,255,0))
lcd.display(self.img)
def colorCalibrate(self, key, r=[(320//2)-(50//2), (240//2)-(50//2), 50, 50]):
for i in range(60):
self.img = sensor.snapshot()
self.img.draw_string(40, 0, "put the color\nin the rect", scale=2,color=(0,255,0))
self.img.draw_rectangle(r)
lcd.display(self.img)
threshold = [50, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0] # Middle L, A, B values.
for i in range(60):
self.img = sensor.snapshot()
self.img.draw_string(40, 0, "be learning...", scale=2,color=(0,255,0))
hist = self.img.get_histogram(roi=r)
lo = hist.get_percentile(0.01) # Get the CDF of the histogram at the 1% range (ADJUST AS NECESSARY)!
hi = hist.get_percentile(0.99) # Get the CDF of the histogram at the 99% range (ADJUST AS NECESSARY)!
# Average in percentile values.
threshold[0] = (threshold[0] + lo.l_value()) // 2
threshold[1] = (threshold[1] + hi.l_value()) // 2
threshold[2] = (threshold[2] + lo.a_value()) // 2
threshold[3] = (threshold[3] + hi.a_value()) // 2
threshold[4] = (threshold[4] + lo.b_value()) // 2
threshold[5] = (threshold[5] + hi.b_value()) // 2
for blob in self.img.find_blobs([threshold], pixels_threshold=100, area_threshold=100, merge=True):
self.img.draw_rectangle(blob.rect(),color=(255,0,0))
self.img.draw_cross(blob.cx(), blob.cy())
self.img.draw_rectangle(r)
lcd.display(self.img)
self.thresholdMap[key] = threshold
def getPosition(self, x, y):
# calculate the closest grid index
minDist = 100000
minIndex = -1
for i in range(len(grid)):
dist = (grid[i][0]-x)**2 + (grid[i][1]-y)**2
if dist < minDist:
minDist = dist
minIndex = i
return minIndex
def setPositon(self, index):
pos = positions[index]
self.robo.geekServo(S8, pos[1])
self.robo.geekServo(S7, pos[0])
def colorTrack(self,key='blue'):
cx=-1
cy=-1
maxArea = 0
for blob in self.img.find_blobs([self.thresholdMap[key]], pixels_threshold=100, area_threshold=100, merge=True, margin=10):
self.img.draw_rectangle(blob.rect())
self.img.draw_cross(blob.cx(), blob.cy())
cx = blob.cx()
cy = blob.cy()
if blob.rect()[2] * blob.rect()[3] > maxArea:
maxArea = blob.rect()[2] * blob.rect()[3]
return (cx, cy)
def tick(self):
self.img = sensor.snapshot()
(rx, ry) = self.colorTrack('blue')
if rx == -1:
self.cachedPosition = []
lcd.display(self.img)
self.setPositon(8)
return
index = self.getPosition(rx, ry)
self.img.draw_cross(grid[index][0],grid[index][1],5,color=(0,255,0))
print(index)
# print history lines
for i in range(len(self.cachedPosition)):
self.img.draw_cross(self.cachedPosition[i][0], self.cachedPosition[i][1],color=(0,100,200))
lcd.display(self.img)
self.setPositon(index)
self.cachedPosition.append((rx,ry))
if len(self.cachedPosition) > 10:
self.cachedPosition.pop(0)
def run(self):
while True:
self.tick()
time.sleep_ms(50)
gc.collect()
ak = AirHockey()
ak.run()
STEP5:程序运行
当冰球运动到KOI的视觉检测范围内,KOI获取到冰球的坐标,控制机械臂运动到对应的位置。如果要准确的控制机械臂的运动,涉及到机械臂运动学逆解,会比较难。因此最终代码中采用了取巧的方式,在冰球桌上规划了20个点,自己通过慢慢调整两个舵机的不同角度,让最终击球装置到达那20个点的位置,当KOI获取冰球的坐标接近20个规划点的位置,就进行击球。
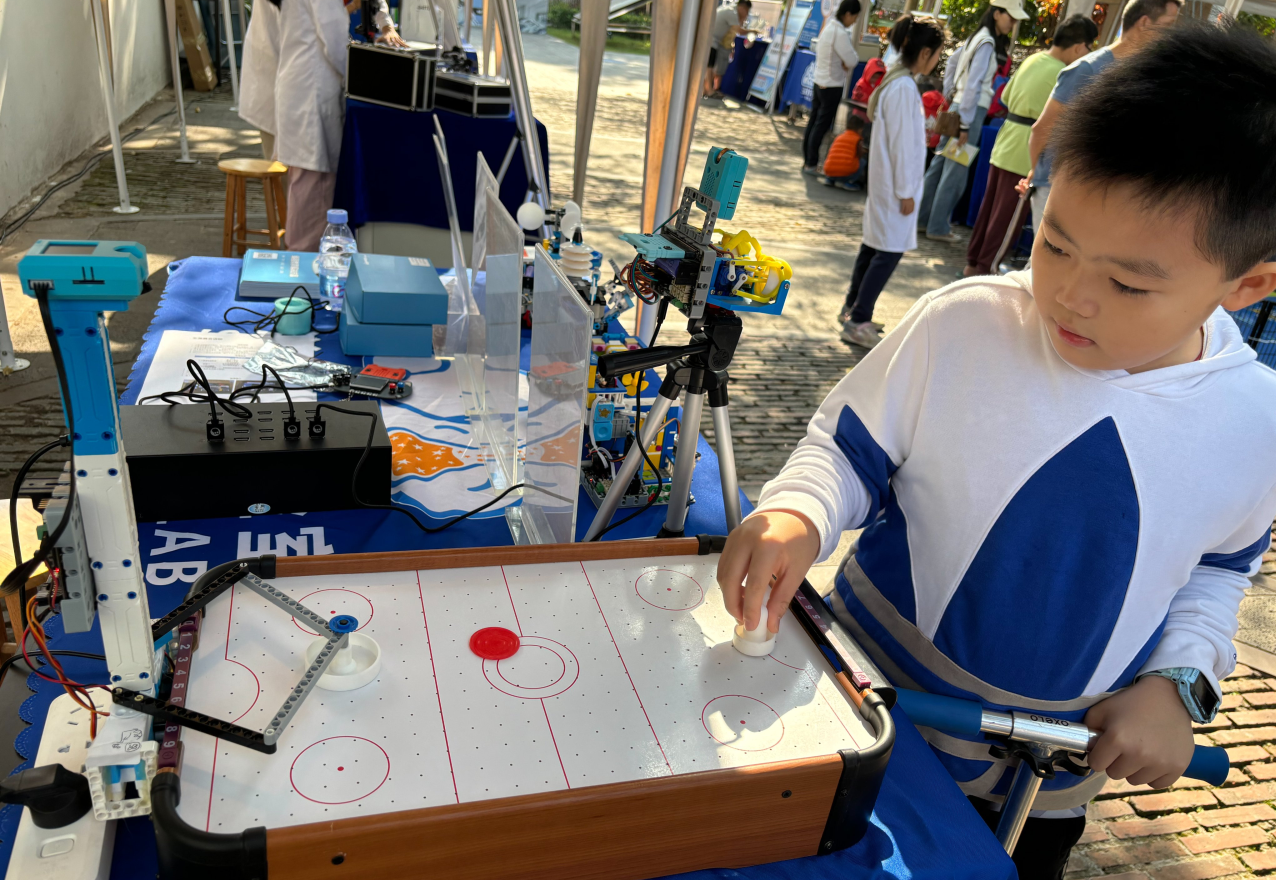

注:如果套件开始正常运行,一段时间后突然摄像头卡主。有可能是供电问题,因为风扇用电较多,应检查是否给风扇模块安装电池,或者电池电量是否足够。